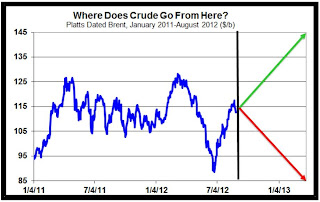
Following on from
earlier conversations with contacts in the trading community about the direction of the Brent crude price versus geopolitics, the Oilholic extended his queries to the
Platts Energy Risk Forum, held in London earlier this week. At the event, Dave Ernsberger, global editorial director of oil coverage at
Platts, summed-up the market mood as we near the final quarter of 2012 (
see graphic above, click to enlarge). “This year has been one of two realities, namely the dire economic climate and upward geopolitical risk. H1 2012 saw anxiety about a war in the Middle East and H2 sees renewed fears of a demand slowdown,” he told delegates.
“The oil price is poised to break away from the mean – but which way? So far it has been chained and shackled in the US$15-20 range either way falling below US$90 and rising above US$115 over the course of this year. The threat of an Iran versus Israel conflict which might draw the US in by default has not gone away. On the other hand a European recession could bring a new oil price crash. Additionally, there is a perception that supply-demand and spare capacity scenarios are not what they are made out to be,” Ernsberger added.
Over a break in proceedings, the Oilholic quizzed the Platts man about the actual influence of the geopolitical or instability premium on the price of the crude stuff and market conjecture about it being broadly neutral for 2013.
“I think the current geopolitical dynamic is fairly well understood at this point. The big touching points which are at play for instance, but not limited to, the US-Iran-Israel issue and the China-Japan and Asia Pacific energy politics have been with us for a while. I feel it is hard to see how those geopolitical arenas will evolve significantly in 2013 because we are at a stalemate point. In a sense, if you look forward they should be neutral,” Ernsberger said.
However, both of us were in agreement that one always needs to be careful about a geopolitical trigger as a single tiny flashpoint could offset the placidness. But from where Ernsberger and the Oilholic sit at present – geopolitical influences are in a kind of suspended animation for next year. The Platts Energy Risk Forum also noted that demand forecasts for 2012 have stabilised and that Chinese demand, on a standalone basis, had slowed considerably. As such, the price outlook for 2013 is overwhelmingly bearish.
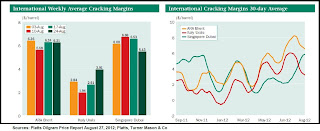
One unintended result of the European crisis brings us to another area of interest - refining. Platts noted that the EU-wide recession is speeding up refinery closures. It suggested that 3 to 5 million barrels per day (bpd) of oil refining capacity is under immediate threat of closure or actually did close recently. Additionally, an estimated 7 million bpd needs to close to adjust for more efficient refining in Asia and Middle East. But the closures are lifting refining margins over the short-term in a business that remains volatile (
see graphic above right, click to enlarge). Ernsberger also brought forth a very valid observation for the readers of this humble blog – the striking similarity between the survival (or vice versa) statistics within the refining and civil aviation sectors.
“Refining and aviation are two industries where it’s a race to the bottom! There is so much competition in both these industries that basically whatever environment you are operating in – even if you are operating in India or China – it’s a race to the bottom…Typically, what you’ll find is that every company would try and stay in the business as long as it can and will only leave when it runs out of money. It’s also why refining and aviation have more bankruptcies than any other sector I can think of,” he said.
At the same forum, it was also a pleasure running into
Dr. Vincent Kaminski, a former
Enron executive who repeatedly raised strong objections to the financial practices at the company prior to its scandal-ridden collapse in 2002. In the aftermath of the scandal, Dr. Kaminski was praised for being among the voices of reason at a company riddled with malpractices. (
For background read Bethany McLean and Peter Elkind’s brilliant book – The Smartest Guys in the Room)
Dr. Kaminski, who is an academic on the faculty of
Houston’s Rice University at present, told the forum that by the time of its collapse Enron had mutated from an energy company to one which traded practically everything and one which was not alone in devising trading strategies based on exploiting geographical constraints.
“Energy markets have evolved over the last 20 years into an integrated global system. Markets for different physical commodities form what can be called a tightly coupled system. While market participants learn and adjust their behaviour in order to survive and prosper in a changing world, the system itself evolves and remains far removed from a stable equilibrium at any point in time,” he added.

Dr. Kaminski also dwelt on the Shale Gas revolution in the US which was decades in the making but transformed the country's energy landscape upon fruition leading to the availability of natural gas in abundance and a dip in gas price-contracts (
see graphic on the left, click to enlarge). “As US production sky-rocketed, conventional wisdom about the possibility of LNG shortages barely five years ago was turned on its head. By April 2012 we even noted a
sub-US$2/mBtu front-month settlement on the NYMEX,” he added.
Later in the afternoon, Dr. Kaminski told the Oilholic that US LNG import terminals currently being prepped to export gas in wake of the shale bonanza could one day be sending tanker-loads to Europe in direct competition with Qatar and Russia.
“On the flipside for the US consumer, the moment a viable gas export market is established for US gas, the impact on the country’s domestic gas market would be a bullish one. That is the nature of market forces,” he added.
When asked about the prospects of shale prospection in Europe – most notably in Poland, Ukraine, Sweden and the UK – Dr. Kaminski said he was a ‘realist’ rather than a ‘sceptic’. “What happened in the US, did not take place overnight. Technology, legislative facilitation and public will – all played a part and gradually fell into place. I do not see it being replicated in Europe over the short term and certainly not with the speed that some are hoping it would,” he concluded.
Just as the Oilholic was winding down from a discussion on shale with Dr. Kaminski, it seems the UK
Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IMechE) was talking up the economic benefits of a British Shale Gale! In a
policy statement circulated to parliamentarians, the IMechE said shale gas was ‘no silver bullet’ for UK energy security but will provide long-term economic benefits in the shape of thousands of jobs.
Dr. Tim Fox, Head of Energy and Environment at IMechE and lead author of the
shale gas policy statement, said, “Shale gas has the potential to give some of the regions hit hardest by the economic downturn a much-needed economic boost. The engineering jobs created will also help the Government’s efforts to rebalance the UK’s skewed economy.”
However, Dr. Fox added that shale gas "is unlikely to have a major impact on energy prices and the possibility that the UK might ever achieve self-sufficiency in gas is remote."
IMechE projects that 4,200 jobs would be created per year over a ten-year drill programme. The engineering skills developed could then be sold abroad, just as the oil and gas experience built up in North Sea oilfields is now being sold across the world. Well, we shall see but that’s all for the moment folks! Keep reading, keep it ‘crude’!
© Gaurav Sharma 2012. Graphic 1: Platts dated Brent – January 2011 to August 2012 © Platts September 2012. Graphic 2: International cracking margins snapshot © Platts / Turner Mason & Co. September 2012. Graphic 3: US Natural Gas futures contract © Dr. Vincent Kaminski, Rice University, Texas, USA /Bloomberg.





