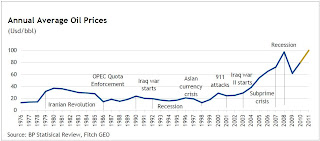
 It has been a month of quite a few interesting reports and comments, but first and as usual - a word on pricing. Both Brent crude oil and WTI futures have partially retreated from the highs seen last month, especially in case of the latter. That’s despite the Libyan situation showing no signs of a resolution and its oil minister Shukri Ghanem either having defected or running a secret mission for Col. Gaddafi depending on which news source you rely on! (Graph 1: Historical average annual oil prices. Click on graph to enlarge.)
It has been a month of quite a few interesting reports and comments, but first and as usual - a word on pricing. Both Brent crude oil and WTI futures have partially retreated from the highs seen last month, especially in case of the latter. That’s despite the Libyan situation showing no signs of a resolution and its oil minister Shukri Ghanem either having defected or running a secret mission for Col. Gaddafi depending on which news source you rely on! (Graph 1: Historical average annual oil prices. Click on graph to enlarge.)
Either way, the 159th OPEC meeting in Vienna which the Oilholic will be attending in a few weeks promises to be an interesting one; we’re not just talking production quotas here. Iranian President Mahmoud Ahmadinejad is also expected to be in Austrian capital – so it should be fun. The market undoubtedly still craves and will continue to crave the quality of crude that Libya exports but other factors are now at play; despite whatever Gaddafi may or may not be playing at.
Contextualising the Libyan situation, Société Générale CIB analyst Jesper Dannesboe notes that Cushing (Oklahoma), the physical delivery point for WTI crude oil, has recently been oversupplied resulting in contango at the very front end of the WTI forward curve.
“This situation is likely to persist until at least mid-2012 as higher supply to Cushing from Canadian oil sands and from North Dakota should result in high Cushing stocks as new pipelines from Cushing to the coast will not be ready until late 2012 at the earliest. This makes it attractive to put on WTI time spreads further out the forward curve at backwardation as they should over time roll into contango,” he wrote in a note to clients.
Dannesboe also observes that while the entire Brent crude oil forward price curve is currently in backwardation (i.e. near-dated prices higher than further-dated prices) out to about 2017, the front-end of the WTI crude oil forward price curve has remained in contango.
The Brent forward curve flipped from contango to backwardation in late February as a result of the unrest in the Middle East & North Africa (MENA). However, contango at the front-end of the WTI forward curve has persisted because WTI's physical delivery point, Cushing (US midcontinent), has remained oversupplied despite a generally tight global market for sweet crude as a result of the loss of Libyan exports, he concludes.
Meanwhile, ahead of the OPEC meeting, the International Energy Agency (IEA) called for “action” from oil producers that will help avoid the negative global economic consequences which a further sharp market tightening could cause. Its governing board meeting last Thursday expressed “serious concern” that there are growing signs the rise in oil prices since September is affecting the economic recovery. As ever, the IEA said it stood ready to work with producers as well as non-member consumers.
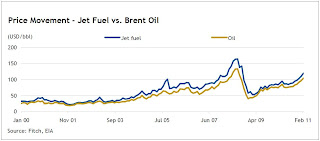 The Oilholic also recently had the pleasure of reading a Fitch Ratings report, authored earlier this month in wake of the Libyan situation, which notes that the airline sector is by far the most vulnerable to rising oil and gas prices of all corporate sectors in the EMEA region given the heavy weight of fuel costs in operating cost structures (20%-30%), execution risks from companies' use of hedging instruments to mitigate their fuel exposure and fierce industry competition. (Graph 2: Price movement - Jet fuel vs. Brent oil. Click on graph to enlarge)
The Oilholic also recently had the pleasure of reading a Fitch Ratings report, authored earlier this month in wake of the Libyan situation, which notes that the airline sector is by far the most vulnerable to rising oil and gas prices of all corporate sectors in the EMEA region given the heavy weight of fuel costs in operating cost structures (20%-30%), execution risks from companies' use of hedging instruments to mitigate their fuel exposure and fierce industry competition. (Graph 2: Price movement - Jet fuel vs. Brent oil. Click on graph to enlarge)
Erwin van Lumich, a Managing Director in Fitch's corporate departments, said, "The gap between the jet fuel price curve and the Brent curve narrowed to approximately 13% during 2010, with airlines in emerging markets generally most exposed to fuel price fluctuations due to a lack of market development for fuel hedging."
It gives food for thought that a temporary impact of the Icelandic volcanic ash can send jitters down the spine of airline investors but the jet fuel pricing spread, airlines’ hedging techniques (or the lack of it) and how it might impact operating margins is mostly raised at their AGMs. Where there are losers, there are bound to be winners but Fitch notes that the ratings of companies in the extractive industries are not expected to benefit from the price increases as the agency uses a mid-cycle pricing approach to avoid cyclical price changes having an impact on ratings. At this stage, Fitch does not anticipate a revision to its mid-cycle price deck to an extent that it would result in rating changes.
Finally, a couple of things about BP. To begin with, BP’s share swap deal with Rosneft failing to meet the May 16th deadline does not imply by default that that deal would not happen. In wake of the objection of AAR – its TNK-BP joint venture partner – there are still issues to be resolved and they will be in the fullness of time contrary to reports on the deal’s demise. A source close to the negotiations (at AAR not Rosneft) says talks are continuing.
Continuing with BP, it finally got recognition that blame for the Macondo incident is not exclusively its. Mitsui (which holds 10% of the well’s licence) and Anadarko (25%) had both blamed accident on BP’s negligence, refusing to pay or bear costs. However, Mitsui finally agreed to settle claims relating to the disaster with BP. It now agrees with BP that it was the result of oversights and mistakes by multiple parties. Undoubtedly, the pressure will now be on Anadarko to settle with BP.
According to US government figures, BP has paid out US$20.8 billion. It has invoiced Mitsui for approximately US$2.0 billion with the Japanese company expected to pay half of that at the present moment in time. A US trial on limitation of liabilities is expected to rule on the issue of gross negligence by parties concerned sometime over Q1 2012. Watch this space!
© Gaurav Sharma 2011. Graphics © Fitch Ratings, May 2011



